|
|
|

|
| Types
availables according to Argensinter
standard
|
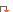 Type
A (DIN 1837) Type
A (DIN 1837) |
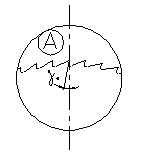
 Type
B (DIN 1838) Type
B (DIN 1838) |
|
|
|
Carbide Grades |
 Micrograno Micrograno |
|
|
|
|
|
Catalog
in PDF Format |
|
|
The
Solid Carbide
Blades catalog is
also available in PDF format. |
|
|
|
 (en español)
(en español)
|
 (em Portugues)
(em Portugues) |
 (in English)
(in English) |
|
|
|
|
|
Side
Cutting or Tooth Form – Side Dump – Tooth Profile
|
|
(based
on DIN 1840 and Argensinter standard)
|
|
Side
Cutting or Tooth Form |
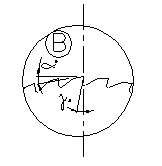
| Type
A |
Type
B |
|
|
|
Cutting
Type |
ﻻ
value
for material |
|
Type
N1 |
Type
H1 |
Type
W1 |
|
A |
5º |
0º |
10º |
|
B |
15º |
8º |
25º |
|
|
Cutting
Type |
α
value
for
material |
|
Type
N1 |
Type
H1 |
Type
W1 |
|
B |
8º |
10º |
12º |
|
|
*1
Conforming to DIN 1836 |
|
Side
Dump |
|

|
|
Tooth
Profile |
|
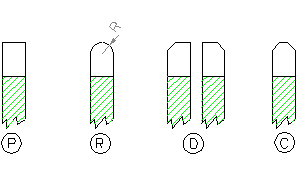 |
| Tooth
Profile |
Description |
| P |
Flat |
| R |
Radial |
| D |
Alternate
Bevel |
| F |
Bevel |
| Saw’s
Identification Code |
The
code structure is formed in the following way: Example: For a
saw blade of diameter A = 100 mm, Thickness E = 0.8 mm,
diameter d1 = 22 mm.
|
| Article
Family |
Article
Subfamily |
Outer
Diameter |
Thickness |
Inner
Diameter |
Tooth |
| Quantity |
Side
Cutting |
Profile |
| F |
I |
100.0 |
0.80 |
22.0 |
Z=100 |
A |
P |
|
F I 100 x 0.80 x 22.0 Z=100 A P
|
|
Code
reference:
Family:
F = Saw
Subfamily:
I = Integral ó S = Weld Edge
Tooth:
Side
Cutting: A ó B (according to DIN 1840 and Argensinter’s
standard).
Tooth
Profile: P = Flat, R = Radial, C =Bevel, D = Alternate
Bevel.
|
|
|
Material
to be Machined. Classification - DIN 1836 |
| Tool |
Description |
| H |
For
particularly hard material and strong-hard material. |
| N |
For
general structural steel, grey cast iron, Non-Ferrous Metals
of average hardness. |
| W |
For
particularly soft and light materials. |
|
Material
|
Type
of Tool |
| Soft
steel - Tensile strength up to 50 kp/mm2 |
N |
|
(W) |
| Medium
steel – Tensile strength up to 80 kp/mm2 |
N |
|
|
| Hard
steel - Tensile
strength up to 100 kp/mm2 |
N |
(H) |
|
| Hard
steel – Tensile strength up to 130 kp/mm2 |
|
H |
|
| Cast
steel |
N |
(H) |
|
| Grey
iron - HB30 bis
hardness up to 180 kp/mm2 |
N |
|
|
| Grey
iron - HB30 bis hardness up to 180 kp/mm2 |
N |
(H) |
|
| Malleable
cast iron |
N |
|
|
| Copper;
Soft Copper Alloy |
(N) |
|
W |
| Dry
copper alloy |
N |
(H) |
|
| Zinc
Alloy |
(N) |
|
W |
| Light
aluminium alloy |
|
|
W |
| Aluminium
alloy, average hardness |
N |
|
(W) |
| Aluminium
alloy, toughened -
Low cutting speed |
N |
|
|
| Aluminium
alloy, toughened - High
cutting speed |
|
|
W |
| Magnesium
Alloy |
(N) |
|
W |
| Plastic,
no laminate |
N |
|
(W) |
| Plastic
laminate |
|
|
W |
The
tool types N, when not in parenthesis, use they in a more
convenient way.
The tool types in parenthesis indicate that they should only
be used in special cases. |
|
A
Note about Side-Cutting or Shaping Cutters
- Type A Engraving (fine-toothed,
V toothed) - DIN
1837 A
This
tooth type, with spaces from 0.8 to 6.3 mm between teeth
according to the saw thickness and dimensions, has been
developed specially for treatment of brittle materials with
tear short shaving. This V-toothed has, thanks to its
engraving teeth, a particularly small shaving bag. As the
result of the relatively small spaces between the teeth, the
type of teeth is only appropriate for small deep cutting or
thin panel materials. It is recommended to use small spaces
between teeth up to 2 mm for small deep cutting up to 3-4 mm.
Larger spaces between teeth can be used for a maximum deep or
maximum cross-sectional up to 15 mm.
Naturally,
other important topics are the materials to cut and the
cutting speed and the corresponding feed. Working with small
feed, it is possible to plunge little deeper cuts without
break teeth risk.
- Type B Engraving (Coarse toothed, spiral toothed) -
DIN 1838 B
This tooth type with spaces
from 3.15 to 12.5 mm between teeth, according to the saw
thickness and the saw dimensions, has relatively large
semicircular shaving bags. which enables shaving generation.
Its area of application is wider than DIN 1837 tooth type.
This
type of teeth is particularly appropriate for cross-sectional
treatment and greater cutting depth. Working with this type of
teeth can enable cross-traversal cutting up to 100 mm,
depending on the dimensions and the space between teeth and
the corresponding feed. Usually, this type of teeth can be
considered the most universal according to DIN. |
|
|
|
|
|
Integral
Hard-Metal Saw Blades
–
DIN 1837
(according
to Argensinter standard) |
|
in mm
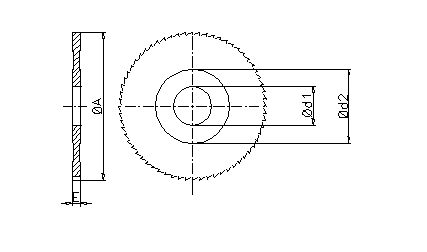
Not
bounded measures are to be chosen oneself.
|
|
|
ØA
|
20
|
25
|
30
|
40
|
50
|
63
|
80
|
100
|
|
Ød1
|
5
|
8
|
8
|
10
|
13
|
16
|
22
|
22
|
|
Ød2
|
10
|
12
|
14
|
18
|
25
|
32
|
36
|
40
|
|
Thicknes
E
|
Number of
teeth Z
|
|
0.30
|
26
|
32
|
40
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
0.40
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
0.50
|
50
|
60
|
64
|
-
|
-
|
|
0.60
|
-
|
-
|
|
0.80
|
84
|
100
|
|
1.00
|
|
1.20
|
|
1.60
|
|
2.00
|
|
2.50
|
|
|
Engraved
The saw blades of this standard have engraved:
A: outside cutting diameter
E: thickness.
d1: inside diameter.
Z: number of teeth. |
|
iTop
|
|
Integral
Hard-Metal Saw Blades
– DIN
1838
(according to Argensinter standard) |
|
in mm
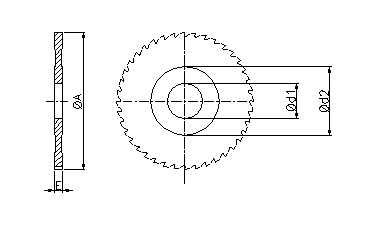
Not
bounded measures are to be chosen oneself.
|
|
|
ØA
|
50
|
63
|
80
|
100
|
|
Ød1
|
13
|
16
|
22
|
22
|
|
Ød2
|
25
|
32
|
36
|
40
|
|
Thickness
E
|
Number
of teeth Z
|
|
0.50
|
50
|
64
|
-
|
-
|
|
0.60
|
50
|
64
|
-
|
-
|
|
0.80
|
50
|
50
|
64
|
-
|
|
1.00
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
64
|
|
32
|
40
|
40
|
50
|
|
1.20
|
40
|
50
|
50
|
64
|
|
32
|
32
|
40
|
50
|
|
1.60
|
40
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
|
24
|
32
|
40
|
50
|
|
2.00
|
32
|
40
|
50
|
64
|
|
24
|
32
|
40
|
40
|
|
2.50
|
32
|
40
|
50
|
50
|
|
24
|
32
|
32
|
40
|
|
3.00
|
32
|
40
|
40
|
50
|
|
24
|
24
|
32
|
40
|
|
4.00
|
32
|
34
|
40
|
50
|
|
20
|
24
|
32
|
32
|
|
|
Engraved
The saw blades of this standard have engraved:
A: outside cutting diameter
E: thickness.
d1: inside diameter.
Z: number of teeth. |
|
|
|
|